Photogrammetry
Scroll
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is a survey technique that allows you to acquire metric data of an object (shape and position).
Photogrammetry
Thanks to photogrammetry we can, by taking many photos around a shape, faithfully reconstruct within a virtual environment, this is useful for an architectural survey or a topographical survey, but also for engineering, geological and archaeological purposes.
Photogrammetry
On a theoretical level, the photogrammetric application involves the resolution of a basic problem which is to relate the three-dimensional object space with the two-dimensional image space in a univocal way, so as to be able to match appropriately chosen discrete points in the two reference systems. This correspondence is obtained by calculating the orientation parameters that govern the transformation. Once the correspondence is obtained, it will be possible to relate any point of the image space to the corresponding point of the object space. The relationship between 2D space and 3D space is known as projectivity.
In order to perform three-dimensional measurements, it is necessary to consider multiple photographs of the object, in which the different representations of the same object point in the various frames are called homologous points. In this way you have a stereoscopic view of the object, similar to what happens in human vision. By collimating the same point from two (even slightly) different points of view, in fact, it is possible to appreciate the three-dimensionality of the object. The base / optimal shooting distance ratio varies between 1/5 and 1/10 and the overlap between successive shots must be between 70% and 80%.
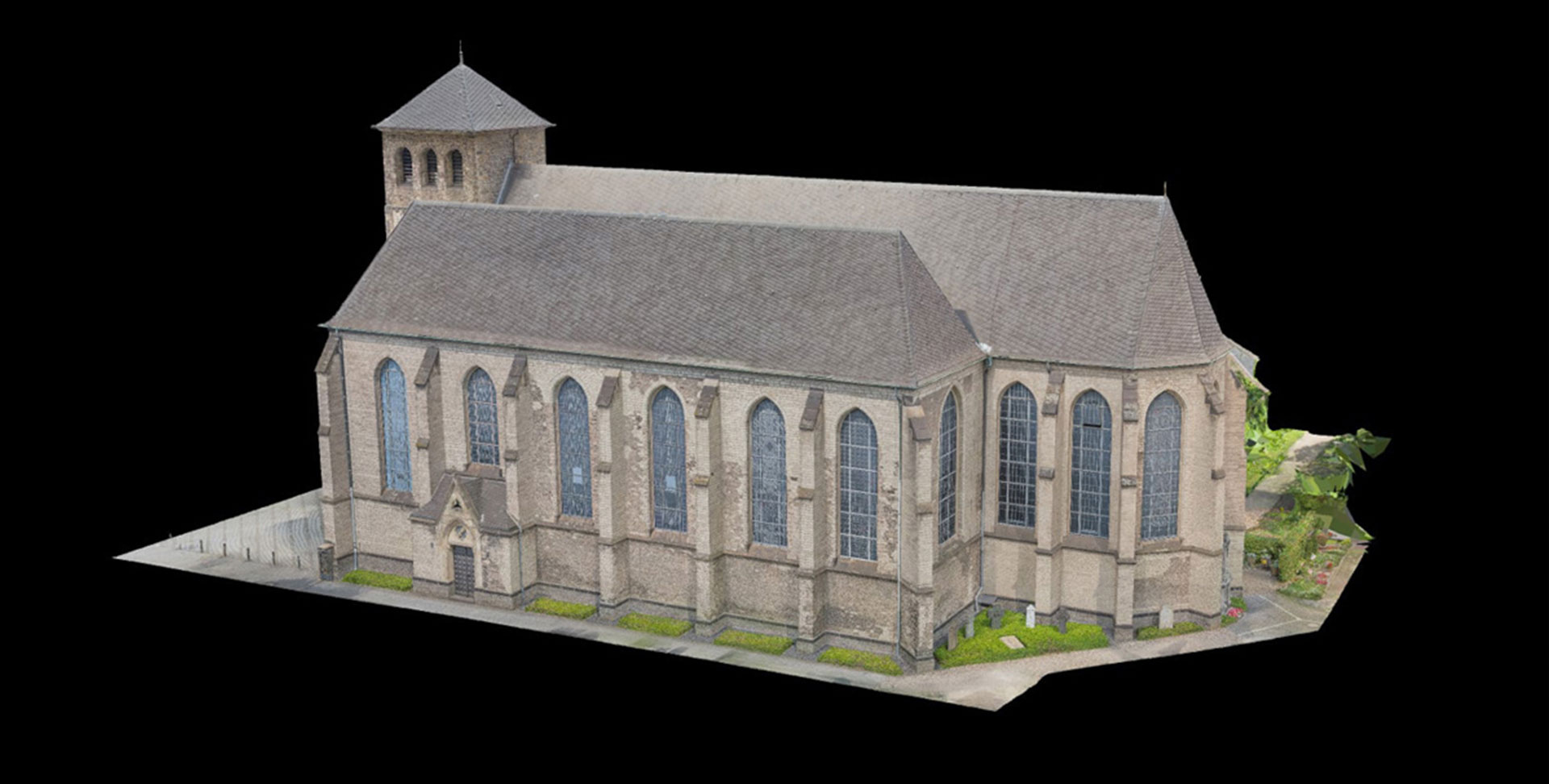

Digital photogrammetry
Digital photogrammetry is conventionally defined as “a set of hardware and software to derive photogrammetric products from digital images using automatic techniques”.
We have gone from analog frames to digital images.
The innovative aspect of digital photogrammetry is represented by the strong automation introduced in the procedures.
This is based on the progressive improvement of the autocorrelation systems (image matching) which, through the recognition of known values or elements in the various frames, allow to automatically identify the homologous points. The level of accuracy currently achieved allows recognition with precisions lower than the pixel size. The correlation operations (relational matching) are performed through the recognition of different entities on the images such as the presence of simple geometric elements (points, lines, etc.) or the relationships between the elements themselves.